Published - 2 months ago | 5 min read
AI in Insurance in 2026: Use Cases, Benefits & AI for Insurance
In 2026, AI in insurance is actively used across underwriting, claims, fraud detection, customer service, and internal operations. Insurers rely on it to process large volumes of information quickly while keeping decision authority with human professionals.
This matters because insurance work compounds. Delays, inconsistencies, or missed risk signals scale into financial losses and customer dissatisfaction. AI in insurance reduces friction by handling volume, summarizing complexity, and improving consistency.
When applied responsibly, AI supports insurance judgment rather than replacing it. Insurers that see value treat AI as operational infrastructure, not a decision-maker.
This matters because insurance work compounds. Delays, inconsistencies, or missed risk signals scale into financial losses and customer dissatisfaction. AI in insurance reduces friction by handling volume, summarizing complexity, and improving consistency.
When applied responsibly, AI supports insurance judgment rather than replacing it. Insurers that see value treat AI as operational infrastructure, not a decision-maker.
What AI in insurance means in 2026
AI in insurance refers to machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and generative models embedded directly into insurance systems. In simple terms, it means software that can read documents, interpret images, summarize information, and surface risk indicators at scale.
In 2026, AI in insurance is rarely a standalone tool. It lives inside underwriting platforms, claims management systems, call center software, and compliance tools. Users often interact with AI outputs without launching a separate product.
The key shift is functional assistance. AI handles unstructured data such as PDFs, medical records, inspection reports, and AI note-taker apps. It organizes information so humans can make faster, better decisions.
This matters because most insurance complexity sits outside spreadsheets. AI shortens the distance between raw information and usable insight.
In 2026, AI in insurance is rarely a standalone tool. It lives inside underwriting platforms, claims management systems, call center software, and compliance tools. Users often interact with AI outputs without launching a separate product.
The key shift is functional assistance. AI handles unstructured data such as PDFs, medical records, inspection reports, and AI note-taker apps. It organizes information so humans can make faster, better decisions.
This matters because most insurance complexity sits outside spreadsheets. AI shortens the distance between raw information and usable insight.
Here’s the quick takeaway:
- AI in insurance processes unstructured data
- Most systems are embedded, not standalone
- Humans remain responsible for decisions
- Most systems are embedded, not standalone
- Humans remain responsible for decisions
How AI in insurance is used in underwriting and pricing
Underwriting uses AI in insurance to evaluate risk faster and more consistently across large volumes of submissions. AI systems ingest structured data alongside unstructured inputs such as inspection reports, emails, medical documents, and historical notes.
Natural language models extract key risk attributes and normalize them into underwriting workflows. This helps underwriters identify missing data, conflicting information, and unusual risk patterns earlier in the process.
Pricing benefits from this structure. AI for insurance supports finer segmentation while keeping pricing logic reviewable. Underwriters see what variables influenced recommendations rather than relying on opaque scores.
In practice, straightforward cases move quickly, while complex cases receive better-prepared human review. This improves throughput without lowering underwriting standards.
Natural language models extract key risk attributes and normalize them into underwriting workflows. This helps underwriters identify missing data, conflicting information, and unusual risk patterns earlier in the process.
Pricing benefits from this structure. AI for insurance supports finer segmentation while keeping pricing logic reviewable. Underwriters see what variables influenced recommendations rather than relying on opaque scores.
In practice, straightforward cases move quickly, while complex cases receive better-prepared human review. This improves throughput without lowering underwriting standards.
How AI for Insurance Improves Claims Handling Workflows
Claims handling relies on AI in insurance to reduce cycle time while maintaining accuracy and fairness. AI systems process first-notice-of-loss submissions, extract relevant facts, and validate information against policy terms.
Computer vision models assess damage from photos and videos. Natural language processing summarizes claimant narratives and adjuster notes into structured summaries.
AI triages claims by complexity, urgency, and potential risk. Simple claims are resolved faster. Complex claims are routed to experienced adjusters with pre-filled context.
This operational leverage explains why claims is often the first area insurers try to scale AI beyond pilots.
Computer vision models assess damage from photos and videos. Natural language processing summarizes claimant narratives and adjuster notes into structured summaries.
AI triages claims by complexity, urgency, and potential risk. Simple claims are resolved faster. Complex claims are routed to experienced adjusters with pre-filled context.
This operational leverage explains why claims is often the first area insurers try to scale AI beyond pilots.
Here’s the quick takeaway:
- AI in insurance shortens claims cycles
- Triage and summarization drive value
- Adjusters retain decision authority
- Triage and summarization drive value
- Adjusters retain decision authority
How insurers apply AI for fraud detection
Fraud detection is one of the clearest economic drivers of AI in insurance, yet it also reveals how difficult scaling actually is.
Machine learning models analyze claim histories, timing patterns, participant networks, and geographic signals to surface anomalies. These systems do not label fraud. They prioritize attention so investigators can focus where risk concentration is highest.
Despite strong results in controlled environments, scale remains limited. Only 7% of insurance companies have successfully brought their AI systems to scale, meaning fraud detection often works well in pockets but inconsistently across the enterprise. Roughly two-thirds of insurers remain stuck in pilots, according to the BCG.
Where insurers succeed, AI connects across claims, underwriting, and external data sources. Where it fails, models remain isolated, reducing impact.
Machine learning models analyze claim histories, timing patterns, participant networks, and geographic signals to surface anomalies. These systems do not label fraud. They prioritize attention so investigators can focus where risk concentration is highest.
Despite strong results in controlled environments, scale remains limited. Only 7% of insurance companies have successfully brought their AI systems to scale, meaning fraud detection often works well in pockets but inconsistently across the enterprise. Roughly two-thirds of insurers remain stuck in pilots, according to the BCG.
Where insurers succeed, AI connects across claims, underwriting, and external data sources. Where it fails, models remain isolated, reducing impact.
How AI supports insurance customer service and distribution
Customer service exposes the gap between AI promise and operational reality.
AI in insurance supports agents by retrieving policy details, claim status, and prior interactions in real time. Virtual assistants handle routine requests, reducing wait times and call volume.
Distribution teams use AI to prepare agents before conversations, summarizing customer context without forcing scripted interactions.
These capabilities are widely available, but unevenly deployed. The market reflects this imbalance. While AI insurance is projected to become a $4.8 billion market by 2032, most insurers have not yet aligned their operating models to absorb that technology consistently.
The value is real. The constraint is execution
AI in insurance supports agents by retrieving policy details, claim status, and prior interactions in real time. Virtual assistants handle routine requests, reducing wait times and call volume.
Distribution teams use AI to prepare agents before conversations, summarizing customer context without forcing scripted interactions.
These capabilities are widely available, but unevenly deployed. The market reflects this imbalance. While AI insurance is projected to become a $4.8 billion market by 2032, most insurers have not yet aligned their operating models to absorb that technology consistently.
The value is real. The constraint is execution
Here’s the quick takeaway:
- AI in insurance improves service responsiveness
- Adoption lags behind capability
- Market growth outpaces operational readiness
- Adoption lags behind capability
- Market growth outpaces operational readiness
How AI is used in internal insurance operations
Internal operations show quieter but more scalable use of AI in insurance.
Finance teams use AI for reconciliation, anomaly detection, and forecasting. Actuarial teams apply AI to scenario modeling and portfolio stress testing. IT teams rely on generative AI to analyze legacy code and accelerate modernization.
These areas succeed because governance is clearer. Fewer regulatory touchpoints. Less emotional customer impact. Stronger internal control.
This is why many insurers see internal AI maturity outpace customer-facing deployments, even though the latter attract more attention.
Finance teams use AI for reconciliation, anomaly detection, and forecasting. Actuarial teams apply AI to scenario modeling and portfolio stress testing. IT teams rely on generative AI to analyze legacy code and accelerate modernization.
These areas succeed because governance is clearer. Fewer regulatory touchpoints. Less emotional customer impact. Stronger internal control.
This is why many insurers see internal AI maturity outpace customer-facing deployments, even though the latter attract more attention.
Why scaling AI in insurance still fails
Scaling AI in insurance fails for reasons that have little to do with models.
The most common barriers include:
- Fragmented data ownership
- Unclear accountability for AI outputs
- Limited frontline trust
- Weak governance structures
The BCG data is telling. While most insurers have pilots, only a small fraction have embedded AI across workflows. This gap explains why outcomes remain uneven despite strong technology.
Insurers that scale successfully treat AI as infrastructure. They assign ownership, train users, and define escalation paths. Without this, AI remains optional rather than operational.
The most common barriers include:
- Fragmented data ownership
- Unclear accountability for AI outputs
- Limited frontline trust
- Weak governance structures
The BCG data is telling. While most insurers have pilots, only a small fraction have embedded AI across workflows. This gap explains why outcomes remain uneven despite strong technology.
Insurers that scale successfully treat AI as infrastructure. They assign ownership, train users, and define escalation paths. Without this, AI remains optional rather than operational.
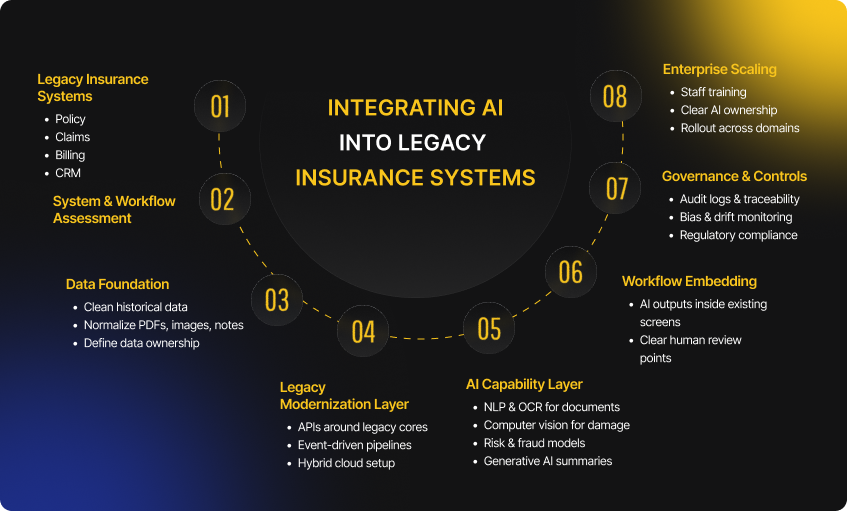
Here’s the quick takeaway:
- AI scale failure is organizational
- Pilots do not equal transformation
- Governance and adoption decide outcomes
- Pilots do not equal transformation
- Governance and adoption decide outcomes
Comparison table: AI use cases in insurance
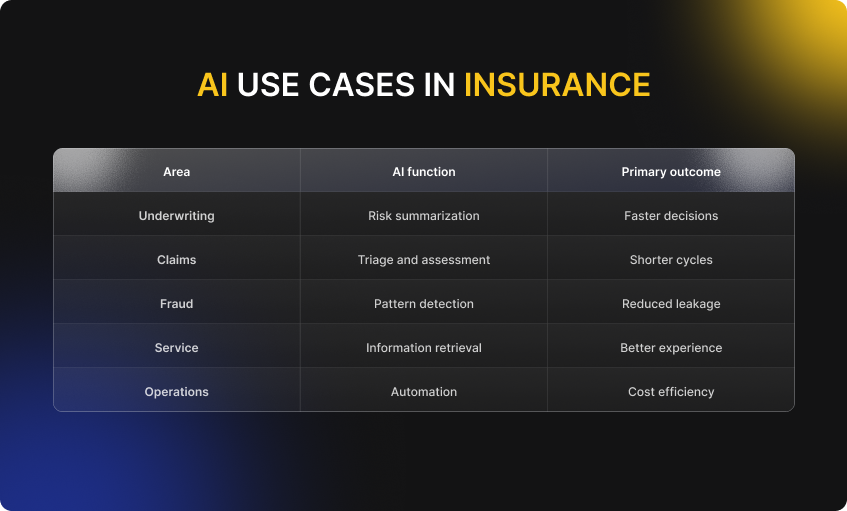
Conclusion
In 2026, AI in insurance is no longer experimental. It is embedded across underwriting, claims, fraud detection, customer service, and internal operations. When applied responsibly, AI for insurance reduces friction, improves consistency, and helps insurers handle scale without removing human judgment. The difference between success and stagnation is not technology, but execution. Insurers that treat AI as operational infrastructure with clear governance, ownership, and adoption are best positioned to improve accuracy, efficiency, and customer trust while remaining fully accountable for decisions.
FAQs
1. How does AI for insurance improve underwriting accuracy?
AI for insurance improves underwriting accuracy by analyzing structured and unstructured data consistently and flagging hidden risk patterns for human review.
2. Is AI in insurance compliant with regulations?
AI in insurance is compliant with regulations when it operates under clear governance, explainability, and human decision oversight.
3. What data does AI in insurance analyze?
AI in insurance analyzes policy data, claims history, documents, images, customer interactions, and external risk signals.
4. Can small insurers use AI for insurance effectively?
Yes, small insurers can use AI for insurance effectively by starting with high-volume workflows using embedded and scalable AI tools.

Written by / Author
Manasi Maheshwari
Found this useful? Share With
Top blogs
Most Read Blogs
Wits Innovation Lab is where creativity and innovation flourish. We provide the tools you need to come up with innovative solutions for today's businesses, big or small.
© 2026 Wits Innovation Lab, All rights reserved
Crafted in-house by WIL’s talented minds

