AI note-taker apps have changed how meetings are documented. Instead of manually typing or listening to recordings later, these tools capture every word, identify speakers, and produce structured notes automatically. OtterAI is one of the best examples of how speech recognition and natural language processing can simplify meeting documentation for individuals and organizations.
If you’re planning to build your own version of an AI note-taker, this guide explains everything from the core architecture to the technical stack, development stages, and features that make such an app reliable and competitive.
If you’re planning to build your own version of an AI note-taker, this guide explains everything from the core architecture to the technical stack, development stages, and features that make such an app reliable and competitive.
What Is OtterAI and How Does It Work?
OtterAI is an intelligent note-taking application that records, transcribes, and summarizes meetings or voice conversations in real time. The system combines automatic speech recognition (ASR) and natural language processing (NLP) to turn spoken content into accurate, shareable notes.
Here’s how it functions step-by-step:
1. The app connects to a microphone or joins a virtual meeting to capture audio continuously.
2. The captured audio is processed through ASR models that convert speech to text.
3. The system identifies who is speaking, separating text by speaker.
4. NLP models then extract keywords, key points, and summaries.
5. All transcriptions and summaries are stored securely on the cloud and can be accessed anytime.
This combination of real-time transcription, speaker detection, and contextual summarization is what makes OtterAI practical for both personal and enterprise users.
Here’s how it functions step-by-step:
1. The app connects to a microphone or joins a virtual meeting to capture audio continuously.
2. The captured audio is processed through ASR models that convert speech to text.
3. The system identifies who is speaking, separating text by speaker.
4. NLP models then extract keywords, key points, and summaries.
5. All transcriptions and summaries are stored securely on the cloud and can be accessed anytime.
This combination of real-time transcription, speaker detection, and contextual summarization is what makes OtterAI practical for both personal and enterprise users.
AI Note-Taking App Market Overview
The market for AI-driven note-taking solutions is growing quickly as remote work and digital meetings become standard. According to SuperRagi, the global note-taking market is expected to reach $11.11 billion by 2025 and continue expanding through 2033.
In 2025, OtterAI reported more than 25 million active users and over $100 million in annual recurring revenue, confirming the rising adoption of AI-based productivity software.
For developers and entrepreneurs, this signals two clear opportunities:
- Businesses are willing to pay for automation that saves time and ensures accuracy.
- The market still has room for new tools offering faster processing, better integration, or privacy-first deployment.
In 2025, OtterAI reported more than 25 million active users and over $100 million in annual recurring revenue, confirming the rising adoption of AI-based productivity software.
For developers and entrepreneurs, this signals two clear opportunities:
- Businesses are willing to pay for automation that saves time and ensures accuracy.
- The market still has room for new tools offering faster processing, better integration, or privacy-first deployment.
Technology Stack for an AI Note-Taker App
Building an app like OtterAI requires a mix of technologies that support real-time audio streaming, AI processing, and secure data management. Below is a realistic tech stack:
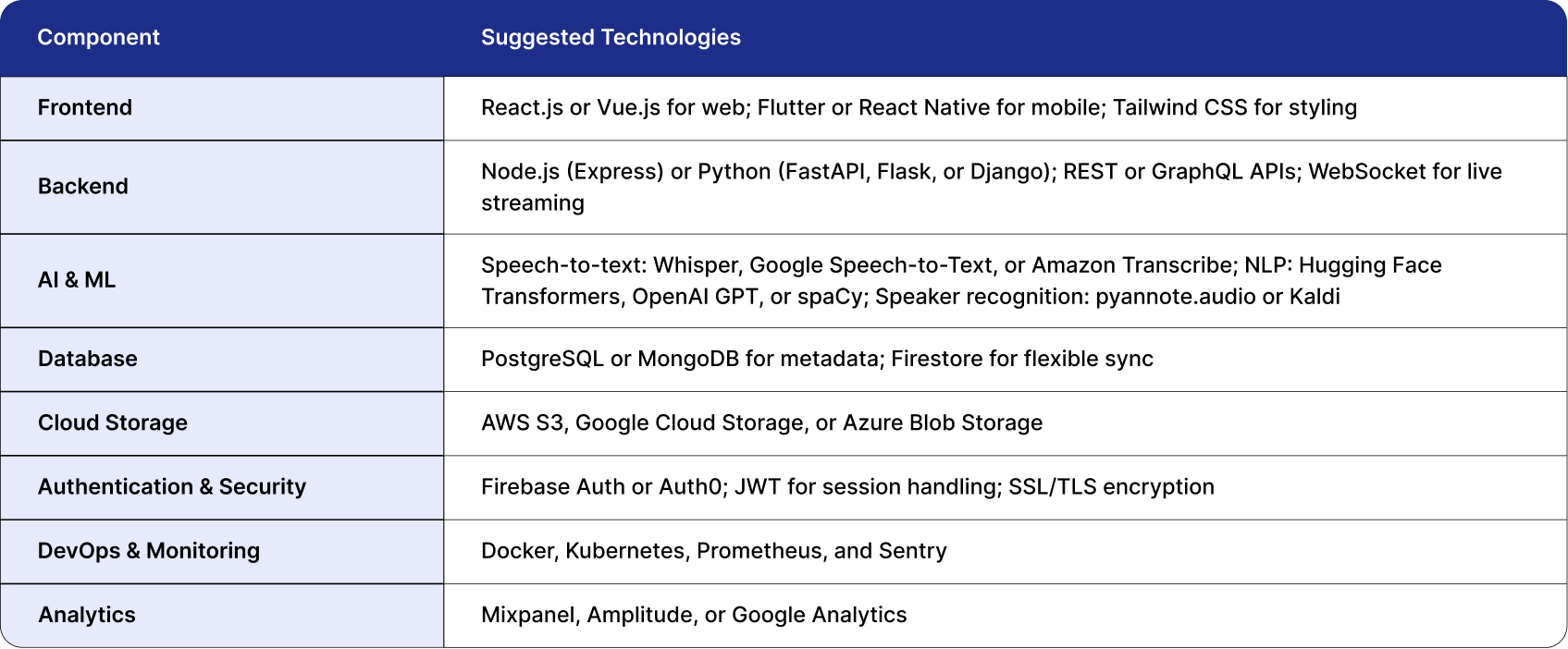
Each part of this stack can be scaled independently, allowing the system to handle thousands of concurrent users and large volumes of meeting data.

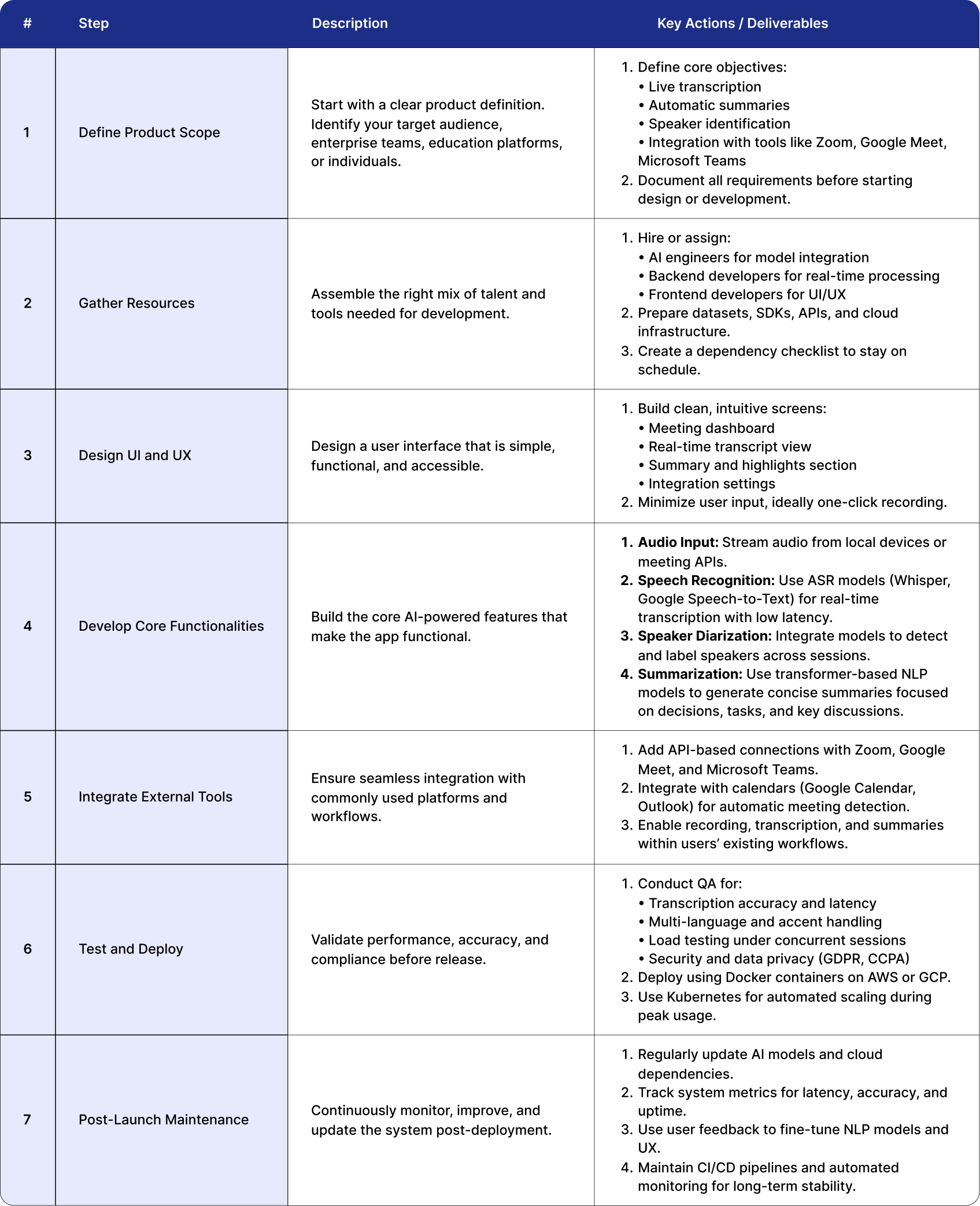
Steps to Build an App Like OtterAI
Building an AI note-taker app like OtterAI needs a structured build process that combines AI modeling, backend engineering, UX design, and cloud optimization into one continuous pipeline. Treat each numbered item as a sprint or set of tasks. Ship something verifiable in every step and measure latency, accuracy, and reliability throughout.
Phase 1 — Foundation and Prototyping
Set the base, validate the pipeline end to end, and prove real-time flow before adding complexity. The goal is a working loop from audio capture to on-screen text.
1. Prepare Infrastructure and Skeleton
- Create a repository structure that supports modular services.
- Provision cloud environments for dev, staging, and production.
- Stand up core services: authentication, PostgreSQL, object storage, basic access control.
2. Audio Capture Module
-Implement reliable capture on web and mobile at 16 kHz mono PCM.
- Chunk audio into small frames, for example 500 ms.
- Add buffering and jitter compensation so short network hiccups do not break the stream.
3. WebSocket Gateway
- Expose a secure streaming endpoint for clients.
- Validate tokens, attach sessions to meetings, and route audio frames to the transcription worker.
4. Prototype ASR Integration
- Start with a hosted ASR API to move fast.
- Stream frames, receive partial and final results, and forward them to the client.
- Capture metrics for end-to-caption latency and error rates.
5. Basic Transcript Viewer
- Render partial lines as they arrive.
- Auto-scroll and update in real time with clear speaker placeholders.
Phase 1 outcome
A basic meeting runs end to end. Audio is captured, text streams live, and a simple viewer displays the transcript.
1. Prepare Infrastructure and Skeleton
- Create a repository structure that supports modular services.
- Provision cloud environments for dev, staging, and production.
- Stand up core services: authentication, PostgreSQL, object storage, basic access control.
2. Audio Capture Module
-Implement reliable capture on web and mobile at 16 kHz mono PCM.
- Chunk audio into small frames, for example 500 ms.
- Add buffering and jitter compensation so short network hiccups do not break the stream.
3. WebSocket Gateway
- Expose a secure streaming endpoint for clients.
- Validate tokens, attach sessions to meetings, and route audio frames to the transcription worker.
4. Prototype ASR Integration
- Start with a hosted ASR API to move fast.
- Stream frames, receive partial and final results, and forward them to the client.
- Capture metrics for end-to-caption latency and error rates.
5. Basic Transcript Viewer
- Render partial lines as they arrive.
- Auto-scroll and update in real time with clear speaker placeholders.
Phase 1 outcome
A basic meeting runs end to end. Audio is captured, text streams live, and a simple viewer displays the transcript.
Phase 2 — Accuracy, Diarization, and Refinement
Once the loop works, focus on transcript quality, speaker labeling, and structured insights. This phase turns raw text into reliable notes.
6. Chunk Stitching and Post-Processing
- Use overlap windows, for example 2 seconds with 0.5 second overlap.
- Merge overlapping outputs, drop duplicates, prefer higher confidence, and restore punctuation and casing.
7. Offline Reprocessing
- After a meeting, reprocess the full audio with a stronger model.
- Replace the provisional transcript and notify clients of improved accuracy.
8. Speaker Diarization Module
- Integrate a diarization pipeline to detect turns and assign speaker labels.
- Input can be full audio or sliding windows.
- Join diarization with transcript segments so each word or sentence has a speaker tag.
9. Live Diarization, Optional and Advanced
- Apply sliding window diarization during the meeting.
- Map new clusters to stable labels such as Speaker A and Speaker B, and keep them consistent.
10. NLP Module for Summaries and Insights
- After transcript finalization, generate bullet summaries, decisions with timecodes, action items with owners and suggested due dates, and keywords or topics.
- Use a strong summarizer tuned to meetings so output is concise and factual.
11. Indexing and Search
- Index sentences or short spans with meeting id, speaker, timestamp, topics, and keywords.
- Provide full-text search, snippet highlighting, and jump-to-time navigation.
Phase 2 outcome
Transcripts are cleaner, speakers are labeled, and teams receive structured highlights that can be searched and shared.
6. Chunk Stitching and Post-Processing
- Use overlap windows, for example 2 seconds with 0.5 second overlap.
- Merge overlapping outputs, drop duplicates, prefer higher confidence, and restore punctuation and casing.
7. Offline Reprocessing
- After a meeting, reprocess the full audio with a stronger model.
- Replace the provisional transcript and notify clients of improved accuracy.
8. Speaker Diarization Module
- Integrate a diarization pipeline to detect turns and assign speaker labels.
- Input can be full audio or sliding windows.
- Join diarization with transcript segments so each word or sentence has a speaker tag.
9. Live Diarization, Optional and Advanced
- Apply sliding window diarization during the meeting.
- Map new clusters to stable labels such as Speaker A and Speaker B, and keep them consistent.
10. NLP Module for Summaries and Insights
- After transcript finalization, generate bullet summaries, decisions with timecodes, action items with owners and suggested due dates, and keywords or topics.
- Use a strong summarizer tuned to meetings so output is concise and factual.
11. Indexing and Search
- Index sentences or short spans with meeting id, speaker, timestamp, topics, and keywords.
- Provide full-text search, snippet highlighting, and jump-to-time navigation.
Phase 2 outcome
Transcripts are cleaner, speakers are labeled, and teams receive structured highlights that can be searched and shared.
Phase 3 — Integrations, UX Polish, and Edge Conditions
Connect to the tools users rely on and harden the experience for real conditions. The product becomes part of the daily workflow.
12. Calendar and Meeting Platform Integration
- Connect Google Calendar or Outlook to auto-detect meetings.
- Integrate APIs for Zoom, Meet, and Teams for direct audio access.
13. Sharing, Permissions, and Export
- Add sharing models (private, link, or organization-level).
- Support multiple export formats (PDF, Markdown, DOCX, SRT).
- Include transcript versioning and edit history.
14. Edge Cases, Noise, and Overlap Handling
- Add noise suppression and silence detection (VAD).
- Handle overlapping speech using separate decoding logic.
- Flag low-confidence sections and allow user correction.
15. UI and UX Polishing
- Visually separate speakers and sections.
- Provide bookmarks and highlight panels for key moments.
- Include real-time summary previews and inline editing.
Phase 3 outcome
The app fits into existing calendars and meeting tools, handles messy audio, and offers a polished, collaborative transcript and summary experience.
12. Calendar and Meeting Platform Integration
- Connect Google Calendar or Outlook to auto-detect meetings.
- Integrate APIs for Zoom, Meet, and Teams for direct audio access.
13. Sharing, Permissions, and Export
- Add sharing models (private, link, or organization-level).
- Support multiple export formats (PDF, Markdown, DOCX, SRT).
- Include transcript versioning and edit history.
14. Edge Cases, Noise, and Overlap Handling
- Add noise suppression and silence detection (VAD).
- Handle overlapping speech using separate decoding logic.
- Flag low-confidence sections and allow user correction.
15. UI and UX Polishing
- Visually separate speakers and sections.
- Provide bookmarks and highlight panels for key moments.
- Include real-time summary previews and inline editing.
Phase 3 outcome
The app fits into existing calendars and meeting tools, handles messy audio, and offers a polished, collaborative transcript and summary experience.
Phase 4 — Hardening, Scaling, and Deployment
Prove reliability at scale, control costs, and meet enterprise expectations for security and compliance.
16. Load Testing and Optimization
- Simulate many concurrent meetings and participants.
- Measure p95 end-to-text latency and summary turnaround.
- Profile bottlenecks such as ASR inference time, network throughput, and database writes.
17. Autoscaling and Architecture Tuning
- Run ASR and summarization on GPU-backed instances or serverless inference endpoints.
- Use message queues to buffer bursty loads.
- Scale transcription, diarization, and NLP independently.
18. Cost Optimization
- Use a hybrid path: fast model during live sessions, stronger model post-meeting.
- Batch small jobs, prune or quantize models when feasible, and leverage spot or reserved instances.
- Run workloads on spot or reserved instances to save costs.
19. Security and Compliance
- Implement data redaction for PII.
- Support “delete meeting” with full physical data purge.
- Enable audit logs and role-based access for enterprise clients.
20. Monitoring and Feedback
- Track metrics like transcription accuracy, latency, and user satisfaction.
- Use dashboards (Grafana, Prometheus) for health monitoring.
- Collect feedback loops to retrain models and improve summaries.
Phase 4 outcome
The product operates reliably under load, costs are predictable, and enterprise controls are in place for security, privacy, and governance.
16. Load Testing and Optimization
- Simulate many concurrent meetings and participants.
- Measure p95 end-to-text latency and summary turnaround.
- Profile bottlenecks such as ASR inference time, network throughput, and database writes.
17. Autoscaling and Architecture Tuning
- Run ASR and summarization on GPU-backed instances or serverless inference endpoints.
- Use message queues to buffer bursty loads.
- Scale transcription, diarization, and NLP independently.
18. Cost Optimization
- Use a hybrid path: fast model during live sessions, stronger model post-meeting.
- Batch small jobs, prune or quantize models when feasible, and leverage spot or reserved instances.
- Run workloads on spot or reserved instances to save costs.
19. Security and Compliance
- Implement data redaction for PII.
- Support “delete meeting” with full physical data purge.
- Enable audit logs and role-based access for enterprise clients.
20. Monitoring and Feedback
- Track metrics like transcription accuracy, latency, and user satisfaction.
- Use dashboards (Grafana, Prometheus) for health monitoring.
- Collect feedback loops to retrain models and improve summaries.
Phase 4 outcome
The product operates reliably under load, costs are predictable, and enterprise controls are in place for security, privacy, and governance.
Process Summary
Advanced and Research Directions
Use these to guide roadmap experiments and deeper differentiation.
- Unified ASR with Diarization
Combined models that predict words and speakers in one pass reduce latency and simplify pipelines.
- Conditioned Whisper with Diarization Embeddings
Conditioning transcription on diarization features improves speaker attribution within the transcript.
- Speculative Decoding for Faster Inference
A small model proposes tokens and a larger model verifies them for speedups without large accuracy loss.
- On-Device Inference
Move parts of the pipeline to mobile for privacy and low latency where hardware permits.

Advanced Features to Make the App Stand Out
To compete effectively, your app must go beyond basic transcription. Consider adding advanced features that enhance usability and value.

These features create a complete experience, positioning your app as a productivity platform rather than just a transcription tool.
Challenges in Building an App Like OtterAI
Building an AI note-taking application involves several technical challenges. Addressing these early ensures better performance and scalability.
1. Background Noise
Meetings often occur in noisy environments. Use noise-reduction filters or pretrained denoising models to clean the audio before transcription. This improves accuracy significantly.
2. Real-Time Performance
Balancing accuracy with speed is difficult. Choose model sizes and inference strategies that provide fast results without compromising reliability. Streaming frameworks such as WebSocket or gRPC reduce latency.
3. Data Privacy and Compliance
Audio recordings contain sensitive information. Apply encryption both in transit and at rest. Make sure your platform is compliant with data privacy laws. Provide users with deletion controls and clear consent mechanisms.
4. Accuracy Across Accents
ASR models may misinterpret accents or overlapping speech. Use diverse datasets or accent-specific fine-tuning to improve recognition quality.
5. Scalability
As your user base grows, infrastructure must handle high audio throughput. Implement autoscaling on your cloud servers and use asynchronous queues such as Kafka or AWS SQS for task distribution.
How to Monetize an AI Note-Taker App
A sustainable revenue model determines long-term success. Common monetization strategies include:
1. Freemium Model
Offer limited transcription minutes or basic summaries for free. Paid users unlock unlimited usage and integrations.
2. Subscription Plans
Provide individual, team, and enterprise plans with varied limits on meeting hours, storage, and AI features.
3. Enterprise Licensing
Offer customized, self-hosted solutions for organizations requiring data control and compliance.
4. In-App Purchases
Sell add-ons such as advanced analytics, multilingual transcription packs, or extended storage.
These models can coexist, letting users upgrade as their needs evolve.
These models can coexist, letting users upgrade as their needs evolve.
Conclusion
Developing an AI note-taker like OtterAI is a technically challenging but achievable project. The foundation lies in combining accurate speech recognition, reliable NLP summarization, and secure cloud storage within a simple user interface. By selecting the right technology stack, optimizing for speed and accuracy,
and addressing privacy and scalability from the start, you can create an app that serves individuals, teams,
and large organizations efficiently. As the demand for AI productivity tools continues to grow,
well-engineered note-taker apps represent a strong opportunity to build products that solve real problems
and sustain long-term business growth.
FAQs
1. Which AI model is best for transcription?
OpenAI Whisper, Google Speech-to-Text, and AssemblyAI are known for high accuracy across multiple languages.
2. How much does it cost to build an app like OtterAI?
Depending on features and infrastructure, development costs typically range from $70,000 to $150,000.
3. Can a non-technical founder build this app?
Yes. You can partner with an experienced AI development team or use APIs for transcription and summarization instead of building models from scratch.
4. Should the app support multiple languages at launch?
You can start with one or two major languages and expand later. Multilingual support is useful for global teams, but can be introduced gradually.
5. How do I maintain accuracy and performance over time?
Collect anonymized usage data, fine-tune models periodically, and monitor latency. Consistent updates are key to maintaining quality.

Written by / Author
Manasi Maheshwari
Found this useful? Share With
Top blogs
Most Read Blogs
Wits Innovation Lab is where creativity and innovation flourish. We provide the tools you need to come up with innovative solutions for today's businesses, big or small.
© 2026 Wits Innovation Lab, All rights reserved
Crafted in-house by WIL’s talented minds

