Published - 2 years ago | 7 min read
ONDC: A Comprehensive Analysis of Technical Structure
The introduction of the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in India signifies a groundbreaking shift in the e-commerce landscape. This initiative, aimed at democratizing digital commerce, moves away from the concentrated market dominance of significant e-commerce giants, promising an open, inclusive, and interoperable framework. With the potential to reshape the entire digital economy, ONDC is a beacon of innovation and equal opportunity.
Understanding ONDC's Foundation: The Technical Blueprint
To appreciate the depth and potential of ONDC, it's crucial to understand its technical components and their interplay.
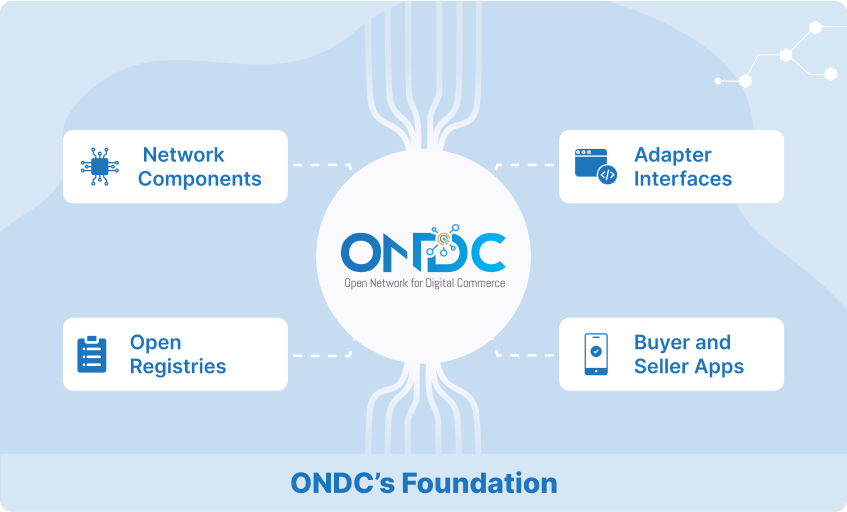
1. Network Components: The Core of ONDC
Registries, The Digital Directories: At the heart of ONDC's architecture are the registries, functioning similarly to a DNS (Domain Name System) on the internet. These registries act as comprehensive directories, listing all participants in the ONDC network, from small retailers to large e-commerce platforms. The registry system ensures that every entity on the network can be uniquely identified and located, much like how a website is found on the internet using its domain name. This mechanism is crucial for establishing seamless connectivity among diverse e-commerce entities, allowing for fluid communication and transaction flows.
Gateways: Managing the E-Commerce Traffic: In the ONDC ecosystem, gateways play a pivotal role during the initial discovery phase of the e-commerce journey, akin to air traffic control towers in an airport. These gateways manage the intricate flow of information across the network, but their function is specialized. When a buyer initiates a search request, the gateway receives this inquiry. The gateway's task is to broadcast this search request to multiple sellers within the relevant domain and specific city the query pertains to.
2. Adapter Interfaces: Bridging Diverse Platforms
The Role of Adapter Interfaces: As the universal connectors in the ONDC ecosystem, Adapter interfaces are akin to universal chargers in electronics. These Adapter interfaces are built as an abstraction layer on top of ONDC, providing an easy method to implement the protocol without delving deep into the complexity of protocol mapping. Adopting open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) as Adapter interfaces is a strategic move that allows various e-commerce platforms to communicate and interact seamlessly, regardless of their underlying technology. This interoperability is crucial for creating a universal language for digital commerce, enabling diverse platforms to connect and transact without technological barriers.
3. Open Registries: The Pillars of Trust and Transparency
Maintaining Integrity and Transparency: Open registries in the ONDC framework serve a role similar to that of a dynamic ledger. They maintain up-to-date records of all network participants and the policies governing them. This continuous updating and maintenance of records are vital for ensuring the network's integrity and reliability. The registries act as the source of truth, ensuring that every participant adheres to the agreed-upon standards and policies. This transparency is very crucial for building trust among network participants and for new entrants who rely on the network's credibility to reach a broader customer base.
4. Buyer and Seller Applications: The Frontend of Transactions
Diversity in Applications: In the ONDC ecosystem, buyer and seller applications are where the transactions occur. These applications vary in complexity and functionality. On the seller side, applications range from simple digital storefronts, where individual sellers can list their products, to complex e-commerce platforms capable of handling various products and services. On the buyer side, applications can be as straightforward as a basic shopping app or as sophisticated as an AI-driven recommendation system, akin to how streaming services recommend content. The diversity in these applications is a testament to ONDC's commitment to inclusivity, allowing entities of all sizes and capabilities to participate in the digital commerce landscape.
ONDC in Action: Illustrative Scenarios
Integration and adaptation to digital platforms are rife with challenges. The WIL ONDC Shopify Adapter is designed to tackle this head-on.

1. Empowering Small Businesses: A local artisan in Jaipur, previously confined to limited markets, can now, through ONDC, showcase their products across multiple buyer apps, significantly broadening their customer base.
2. Enhancing Consumer Choices: A consumer in Mumbai seeking a specific gadget isn't limited to a single platform's inventory. ONDC enables access to various seller applications, echoing the convenience of aggregators in the travel industry.
The Policy Ecosystem: Shaping Digital Commerce

1. Promoting Fair Play with Minimalistic Policies
a. Principles of Net Neutrality in E-Commerce: ONDC's policy framework is heavily inspired by net neutrality principles. Just like net neutrality advocates for equal access to internet resources, ONDC aims to ensure that all digital commerce players, regardless of size or influence, have equal access to the market. This approach intends to dismantle the monopolistic structures in today's e-commerce ecosystems.
b. Building a Balanced Marketplace: The essence of ONDC's policy framework is to strike a balance between being business-friendly and consumer-centric. This involves creating policies that do not overburden sellers with regulatory complexities while safeguarding consumer interests. The policies aim to streamline operations, reduce entry barriers for new sellers, and protect consumers from unfair trade practices.
2. Data Policy: A Fine Balance Between Privacy and Openness
a. Embracing India's Data Protection Standards: ONDC's Approach to Data Privacy: The ONDC framework is designed to comply with the Information Technology Act 2000, focusing on creating a secure and equitable digital marketplace. Unlike the GDPR's approach, ONDC emphasizes facilitating access to e-commerce data for all market players, particularly benefiting smaller entities lacking larger competitors' extensive data insights. This access allows for a level playing field where insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and pricing can spur innovation and competitiveness across the board.
Key to ONDC's data policy is its anticipation of India's evolving personal data protection regulations. The policy is prepared to align with the upcoming regulations, ensuring responsible handling of personally identifiable information and clarifying consent protocols. This proactive stance safeguards user privacy while promoting a transparent and inclusive e-commerce ecosystem.
By democratizing data access, ONDC aims to foster a vibrant marketplace where smaller players can compete effectively, leveraging shared insights to enhance offerings and consumer engagement.
Key to ONDC's data policy is its anticipation of India's evolving personal data protection regulations. The policy is prepared to align with the upcoming regulations, ensuring responsible handling of personally identifiable information and clarifying consent protocols. This proactive stance safeguards user privacy while promoting a transparent and inclusive e-commerce ecosystem.
By democratizing data access, ONDC aims to foster a vibrant marketplace where smaller players can compete effectively, leveraging shared insights to enhance offerings and consumer engagement.
b. Ensuring Transaction Data Confidentiality: The policy dictates that transaction data should remain exclusively between the seller and buyer applications. ONDC will not store or access any details of the transactions, reinforcing its commitment to maintaining the privacy and integrity of commercial exchanges on its platform. This approach aligns with best practices for data protection and builds trust within the ONDC ecosystem, ensuring that sensitive financial and personal information is safeguarded against unauthorised access or misuse. By strictly limiting the visibility of transaction data to the parties directly involved, ONDC fosters a secure environment for digital commerce, encouraging wider participation from both businesses and consumers.
Challenges and Solutions in ONDC's Journey
1. Technical and Operational Challenges
Integrating Diverse Platforms: One of the most daunting tasks is integrating a wide array of platforms, each with its unique technology stack and operational protocols. Ensuring these disparate systems work seamlessly within the ONDC framework requires extensive standardization.
Solutions: The proposed solution includes a phased implementation approach, where integration is gradually scaled up. Extensive testing in controlled environments and iterative policy refinement based on feedback and performance metrics are crucial. This phased approach allows for ironing out technical glitches and ensures a smooth transition for all participants.
Solutions: The proposed solution includes a phased implementation approach, where integration is gradually scaled up. Extensive testing in controlled environments and iterative policy refinement based on feedback and performance metrics are crucial. This phased approach allows for ironing out technical glitches and ensures a smooth transition for all participants.
2. Ensuring Participation and Adoption:
Incentivizing Existing E-commerce Players: The challenge lies in convincing established e-commerce entities to transition to this new model, which may initially seem disruptive to their existing operations.
Strategies for Adoption: To address this, ONDC could offer incentives like reduced transaction fees, access to a broader customer base, and technical support. Additionally, endorsements and support from government bodies could add credibility and encourage participation.
Strategies for Adoption: To address this, ONDC could offer incentives like reduced transaction fees, access to a broader customer base, and technical support. Additionally, endorsements and support from government bodies could add credibility and encourage participation.
The Road Ahead: Scaling and Evolving the ONDC Ecosystem

1. Expansion Strategies
Involving More Participants: As ONDC matures, its expansion strategy involves incorporating more participants, thereby increasing transaction volumes and enhancing the network's robustness.
Collaborations and Innovations: Partnerships with global technology leaders and continuous technological innovation will be crucial. This includes developing new features, improving platform scalability, and ensuring the network's security and reliability.
2. Global Implications and Leadership
Adapting to Various Market Dynamics: The flexibility and adaptability of the ONDC framework to different market environments and consumer behaviours make it a viable model for global standards in digital commerce.
Conclusion
ONDC is a technical infrastructure and a transformative vision for a more inclusive and vibrant e-commerce ecosystem in India. By fostering an open network that promotes innovation and fair competition, ONDC has the potential to redefine the e-commerce sector and catalyze a shift in the entire digital economy. As this initiative unfolds, its success could serve as a model for other nations, showcasing the transformative power of open digital commerce networks.

Written by / Author
Manasi Maheshwari
Found this useful? Share With
Top blogs
Most Read Blogs
Wits Innovation Lab is where creativity and innovation flourish. We provide the tools you need to come up with innovative solutions for today's businesses, big or small.
© 2026 Wits Innovation Lab, All rights reserved
Crafted in-house by WIL’s talented minds

