In the world of Artificial Intelligence, two recent developments have particularly captured widespread attention: Large Language Models and Large Behavior Models. While both represent advances in AI, they differ significantly in their formulations and applications. Large Language Models focus primarily on comprehending and creating language - analyzing text and generating responses at a vast scale. Comparatively, Large Behavior Models go beyond by incorporating principles of action and experience-driven learning. By integrating behavioral data over time, these models can understand and actively engage with the world in human-like ways. Let us explore in deeper detail the distinguishing techniques, growing uses, and diverging impacts of these two innovative model categories and how each uniquely reconfigures AI's anticipated trajectory.
Understanding Large Language Models (LLMs)

Large language models like LLMs were explicitly made to process and understand human language. These AI-based systems are fed vast amounts of textual data for training purposes. They can discern not only the regularities within natural languages themselves but also their structure. LLMs generate coherent responses in natural language that integrate with their present context in a way we call 'mart' by hashing through vast amounts of text data, such as those from books, websites, and literature.
The typical architecture for an LLM is based on a transformer model, a neural network. openAI's GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) series, Google's BERT, and Meta's LLaMA are all influential LLMs that can hold human-like conversations, grade essays for you, summarize topics of discourse, and answer questions.
The typical architecture for an LLM is based on a transformer model, a neural network. openAI's GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) series, Google's BERT, and Meta's LLaMA are all influential LLMs that can hold human-like conversations, grade essays for you, summarize topics of discourse, and answer questions.
Key Abilities of LLMs
LLMs are strong in the following areas:
1. Text Generation: LLMs can produce coherent and contextually meaningful natural sentences using the data from their vast amounts of text.
2. Translation: LLMs are highly accurate in translating text between languages.
3. Summarization: They can condense long texts into summaries that retain the essential content.
4. Sentiment Analysis: LLMs analyze text to give a sense (or sensation) of the situation, emotion, or mood.
These abilities mean that LLMs are valuable in customer support, content generation, and research work. However, there's a snag: LLMs are limited to language and do not understand the outside world. That's where LBMs come in.
1. Text Generation: LLMs can produce coherent and contextually meaningful natural sentences using the data from their vast amounts of text.
2. Translation: LLMs are highly accurate in translating text between languages.
3. Summarization: They can condense long texts into summaries that retain the essential content.
4. Sentiment Analysis: LLMs analyze text to give a sense (or sensation) of the situation, emotion, or mood.
These abilities mean that LLMs are valuable in customer support, content generation, and research work. However, there's a snag: LLMs are limited to language and do not understand the outside world. That's where LBMs come in.
Understanding Large Behavior Models (LBMs)
By integrating language capability with behavior research, LBMs seek to return to nature and meet real-world demands in the highest form. LBMs do not just understand words; they watch actions. They analyze physical interactions, too, mimicking human behavior. When these abilities of language and behavior can be combined ontologically in the same organism, they make for a new family of robots that is at home equally in human society and nature.
A cooking robot is a case in point. The robot learns to cook food by watching how humans do it. It follows programmed instructions, observes chopping techniques, learns what temperature to heat up such foods, and suits itself to the user's taste. LBMs use multi-modal data (text, images, videos, and sensor data) to analyze complex behaviors. They can see, hear, and feel in conjunction with judgment words, and this is progress on LLMs limited by text data alone.
A cooking robot is a case in point. The robot learns to cook food by watching how humans do it. It follows programmed instructions, observes chopping techniques, learns what temperature to heat up such foods, and suits itself to the user's taste. LBMs use multi-modal data (text, images, videos, and sensor data) to analyze complex behaviors. They can see, hear, and feel in conjunction with judgment words, and this is progress on LLMs limited by text data alone.
Key Abilities of LBMs
LBMs excel in:
1. Behavioral Observation: They watch and replicate human activities.
2. Real-Time Adaptation: LBMs can modify their actions based on real-time feedback.
3. Interactive Learning: LBMs ask and learn from responses, constantly improving their actions.
4. Multi-Modal Data Fusion: They process different kinds of data (text, images, sound) together to reach well-informed decisions.
LBMs are particularly suited to scenarios where AI has to respond to physical stimuli and sudden environmental changes, like a robot changing its grip when lifting something or medical AI assessing patient behavior to recommend individualized treatment.
1. Behavioral Observation: They watch and replicate human activities.
2. Real-Time Adaptation: LBMs can modify their actions based on real-time feedback.
3. Interactive Learning: LBMs ask and learn from responses, constantly improving their actions.
4. Multi-Modal Data Fusion: They process different kinds of data (text, images, sound) together to reach well-informed decisions.
LBMs are particularly suited to scenarios where AI has to respond to physical stimuli and sudden environmental changes, like a robot changing its grip when lifting something or medical AI assessing patient behavior to recommend individualized treatment.
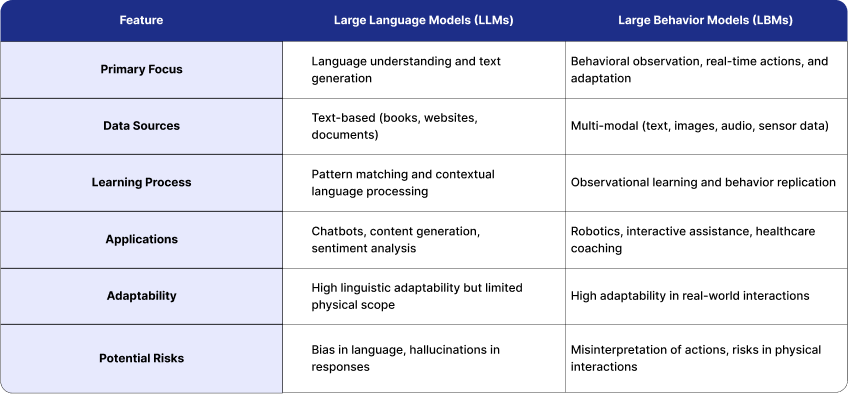
Key Differences Between LLMs and LBMs
Real-World Examples and Use Cases
Large Language Models (LLMs)
1. Customer Support Chatbots: LLMs can be used to create a customer support bot system that can answer complex queries, respond in human-friendly language, and determine customers' emotions. They analyze historical chat data and recommend responses or forward cases to human agents when necessary.
2. Content Generation: LLMs such as GPT-4 are common in content generation, from writing articles to developing social media posts. LLMs assist marketers in producing targeted content that is consistent with brand messaging and tone.
3. Medical Research Summaries: An LLM can scan a massive database of studies, summarize results, and help researchers by indicating important findings or relevant information. LLMs can offer helpful abstractions for dense information fields, such as oncology or genomics.
4. Machine Translation: Google Translate and other similar tools heavily depend on LLMs to give precise translations of a large number of languages together so that businesses can communicate globally.
2. Content Generation: LLMs such as GPT-4 are common in content generation, from writing articles to developing social media posts. LLMs assist marketers in producing targeted content that is consistent with brand messaging and tone.
3. Medical Research Summaries: An LLM can scan a massive database of studies, summarize results, and help researchers by indicating important findings or relevant information. LLMs can offer helpful abstractions for dense information fields, such as oncology or genomics.
4. Machine Translation: Google Translate and other similar tools heavily depend on LLMs to give precise translations of a large number of languages together so that businesses can communicate globally.
Large Behavior Models (LBMs)
1. Robotics: LBMS is essential in robotics. For instance, Toyota is researching how LBMs can assist robots in learning dexterous tasks such as assembly or meal preparation by watching humans do the same. These robots aren't just programmed to follow instructions — they learn and respond in real-time according to their environment.
Healthcare Coaching: LBM concepts are applied to tailor health campaigns (e.g., Lirio). Through patient data analysis, LBMs provide personalized recommendations for healthy behavior modifications while tracking changes and fostering compliance. This could assist with weight management, chronic disease treatment, and mental health support.
2. Household Robots: Envision a robot that would tidy up your home, prepare food, and complete the chores associated with running a household. These robots would need LBMs to navigate around furniture, interpret user preferences, and adapt their actions to information that they gained after days of interactions.
3. Training and Education: LBMs have found great applications in education, especially for skills that require hands-on practice, such as cooking, painting, and carpentry. LBM uses observation and student interactions to deliver real-time feedback and personalized tutoring, which results in better learning processes.
Healthcare Coaching: LBM concepts are applied to tailor health campaigns (e.g., Lirio). Through patient data analysis, LBMs provide personalized recommendations for healthy behavior modifications while tracking changes and fostering compliance. This could assist with weight management, chronic disease treatment, and mental health support.
2. Household Robots: Envision a robot that would tidy up your home, prepare food, and complete the chores associated with running a household. These robots would need LBMs to navigate around furniture, interpret user preferences, and adapt their actions to information that they gained after days of interactions.
3. Training and Education: LBMs have found great applications in education, especially for skills that require hands-on practice, such as cooking, painting, and carpentry. LBM uses observation and student interactions to deliver real-time feedback and personalized tutoring, which results in better learning processes.

Why Are LBMs the Next Big Thing in AI?
LLMs transformed how we interact with computers by making conversations more natural and human-like. However, LBMs take AI further, allowing it to observe, learn, and act in the real world. Imagine an AI that doesn't just respond to your words but observes your actions, asks clarifying questions, and performs a task with physical precision.
For example, an LBM could watch a skilled worker operate a machine in a manufacturing plant and replicate those actions. Over time, the LBM could even identify ways to optimize the process, bringing unprecedented flexibility and intelligence to manufacturing.
For example, an LBM could watch a skilled worker operate a machine in a manufacturing plant and replicate those actions. Over time, the LBM could even identify ways to optimize the process, bringing unprecedented flexibility and intelligence to manufacturing.
Challenges and Considerations
LLMs pose some challenges, and so do LBMS:
LLMs
The LLMs have language bias, hallucination, and data ethics issues. Because they are learned from existing text data, this can lead to perpetuating harmful social biases or generating misleading facts.
LBMs
LBMs themselves have their issues, especially when it comes to how physical agents may interpret actions. For example, an LBM may think that dropping a knife while cooking is part of the recipe as it observes a human doing so. Ensuring correct and secure behavior interpretations is significant.
Another technical challenge of LBMs is data integration with multi-modal information, where complex and potentially time-consuming fusion may be needed from different domains. Safety: Misinterpretations (in real-time tasks) could alter the effectiveness of the task at hand — this is especially important in sectors like healthcare and autonomous driving. Moreover, the ethical implications of AI, including its capability for autonomous decision-making in complex scenarios, require thorough oversight and governance.
Another technical challenge of LBMs is data integration with multi-modal information, where complex and potentially time-consuming fusion may be needed from different domains. Safety: Misinterpretations (in real-time tasks) could alter the effectiveness of the task at hand — this is especially important in sectors like healthcare and autonomous driving. Moreover, the ethical implications of AI, including its capability for autonomous decision-making in complex scenarios, require thorough oversight and governance.
Outlook: Union of LLMs and LBMs?
The integration of LLMs and LBMs gives rise to amazing possibilities. AI systems that bridge the divide between grasping and doing will combine what LLMs do with language —generate and process words—with LBMs, which do actions but not words. Such hybridization could pave the way for more advanced AI companions in healthcare, assistive robotics, and creativity (art and music).
Combining these features could enable robot-human interaction in the above complexities, where robots could understand verbal commands with rich contextual information when listening and reading gestures without requiring commands to change actions. For example, a robot utilized in healthcare may listen to a patient describe their symptoms, identify physical indicators, and offer instant customized assistance.
Combining these features could enable robot-human interaction in the above complexities, where robots could understand verbal commands with rich contextual information when listening and reading gestures without requiring commands to change actions. For example, a robot utilized in healthcare may listen to a patient describe their symptoms, identify physical indicators, and offer instant customized assistance.
Conclusion
LLM (Large Language Model) and LBModel (Large Behavior Model): Each type benefits AI. LLMs naturally complement LBMs as they enable AI to understand and communicate in natural language, while the latter expands their horizons by incorporating behavior and interaction with the physical world. Put them together, and they make up the two halves of a complete intelligence system — one that can comprehend and another that can perform.
As LBMs become more sophisticated, AI systems may respond to our needs, observe us in everyday situations, and learn from them to improve. Such evolution could bring about huge innovations necessary for AI to become a well-integrated part of our lives, such as home assistants, workplace robots, and health advisors.
To sum up, AI cannot talk or act; the future of AI should find its place somewhere between all talking and no talking capabilities again, that is, having machines not only to do both with insight and intelligence but also to adjust their behavior.
As LBMs become more sophisticated, AI systems may respond to our needs, observe us in everyday situations, and learn from them to improve. Such evolution could bring about huge innovations necessary for AI to become a well-integrated part of our lives, such as home assistants, workplace robots, and health advisors.
To sum up, AI cannot talk or act; the future of AI should find its place somewhere between all talking and no talking capabilities again, that is, having machines not only to do both with insight and intelligence but also to adjust their behavior.

Written by / Author
Manasi Maheshwari
Found this useful? Share With
Top blogs
Most Read Blogs
Wits Innovation Lab is where creativity and innovation flourish. We provide the tools you need to come up with innovative solutions for today's businesses, big or small.
© 2026 Wits Innovation Lab, All rights reserved
Crafted in-house by WIL’s talented minds

